Artificial intelligence (AI) has grown in prominence and importance across a broad range of industries, including dentistry. It can imitate human intelligence to make complex predictions and decisions in the healthcare sector, especially in endodontics. AI models, such as convolutional neural networks and/or artificial neural networks, have shown a variety of applications in endodontics, including studying the anatomy of the root canal system, forecasting the viability of dental pulp stem cells, measuring working lengths, pinpointing root fractures and periapical lesions, and forecasting retreatment procedure success.
This technology’s potential uses include scheduling, patient care, drug-drug interactions, prognostic diagnosis, and robotic endodontic surgery. In endodontics, AI has proven accuracy and precision in disease detection, assessment, and prediction. AI can help progress endodontic diagnosis and therapy, which can improve endodontic treatment outcomes. However, before incorporating AI models into regular clinical operations, it is necessary to further validate their cost-effectiveness, dependability, and applicability.
Table of Contents
ToggleIn this article we will read:
- So what is this “AI” exactly?
- AI and dentistry
- How is AI used in dentistry?
- Dental diagnosis:
- Planning treatments:
- Dentistry technologies:
- Whitening teeth:
- Will AI replace dentists?
- Final words:
So, what is this “AI” exactly?
The ability of machines to carry out tasks that ordinarily require human intelligence is known as artificial intelligence (AI). The word “AI” is not brand-new; the idea behind it dates back to 1950. However, it wasn’t until 20 years ago that it started to be used as a tool. Big data (derived from digital devices), computational power, and AI algorithms, the three pillars of current AI technology, have developed rapidly over the past 20 years, and as a result, AI applications have begun to improve people’s lives.
AI and dentistry
All dental specialties, including operative dentistry, periodontics, orthodontics, oral and maxillofacial surgery, and prosthodontics, have adopted AI. Due to limitations in data availability, data uniformity, and computational power for handling 3D data, other tasks are not as applicable as image-based tasks in the field of dentistry. The majority of AI applications in dentistry focus on diagnosis based on radiographic or optical images. Evidence-based dentistry (EBD) is recognized as the gold standard for the decision-making of dental professionals, while AI machine learning (ML) models learn from human expertise.
ML is currently utilized for:
- dental image interpretation by automation (radiographs, CBCT, and MRI scans)
- Recommendations for treatment
- Predictions of future dental diseases
What’s best?
Machine learning algorithms have shown to outperform dentists in diagnosing dental decay or predicting whether a tooth should be removed, kept, or given restorative therapy.
AI can be applied in a variety of ways to enhance the precision, efficiency, and efficacy of dental care, from diagnosis to treatment planning.
How is AI used in dentistry?
Although it may be difficult to see how a computer can be taught to recognize caries by showing it numerous images of caries, it is actually very similar to how we humans do it. As they do not naturally recognize dogs, cats, and cars, newborn babies must also learn to classify visual information into objects. Because of how closely its structure and functioning resemble that of an animal or human nervous system, the programming language used in computer vision is referred to as a “neural network”. The computer receives an unprocessed image in the shape of a sizable assemblage of pixels, much like the human retina with its rods and cones. Edges, gradients, amounts and locations of color, light and dark, and other relationships are discovered between them, and the program compares these relationships with an internal database of object-related relationship sets in an effort to find a close match.
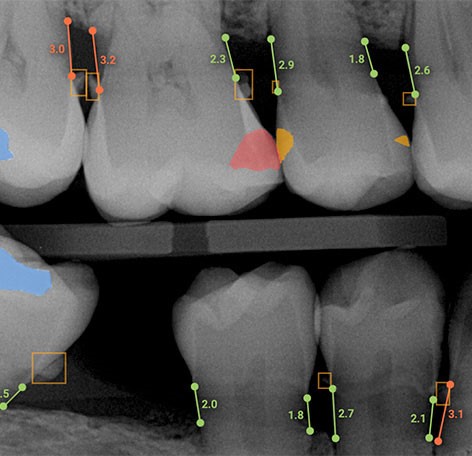
The difficult aspect is developing that internal catalog in the first place. The method is known as “deep learning,” a somewhat dramatic phrase for discovering mathematical similarities in a large number of visual records of the same class of object. The computer, which has learned from 10,000 pictures of various cats, can identify any new cat and will not be fooled by a catlike dog or other feline. The outcomes are astoundingly exact. The computer will identify not just any cat, but a specific cat; not just any face, but your face, even if it is turned sideways, in the middle of a crowd, or partially obscured by your N95.
Dental radiologists annotated thousands of radiographs to teach a machine learning system for use in dentistry. The AI learned to recognise the visual signatures of a broad range of both normal and abnormal conditions by studying those annotated radiographs. Naturally, the annotators did not always concur on everything. When they disagreed, the AI noted the difference as an uncertainty. As a result, a machine has been created that embodies the combined skill of a large team of expert radiograph readers and is capable of learning and refining its abilities through continuous feedback.
Dental diagnosis:
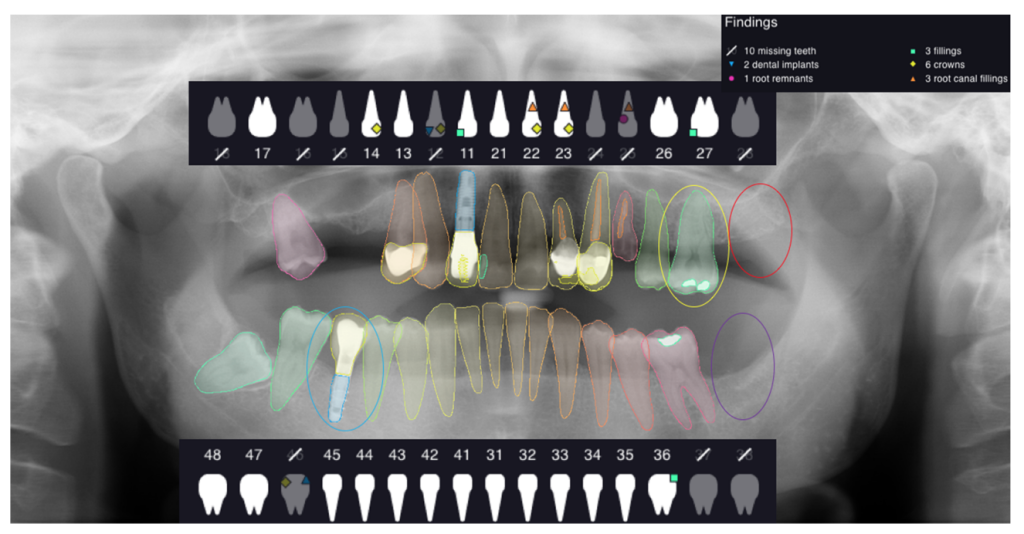
Dental diagnosis is one field where AI is already in use. Dental X-rays and CT scans can be analyzed by AI algorithms to look for patterns or anomalies that a human dentist might overlook. AI, for instance, can identify early indications of oral cancer, gum disease, and tooth decay, allowing dentists to identify and address these conditions before they worsen.
Planning treatments:
AI is also useful for organizing treatments. AI algorithms can suggest individualized treatment plans that are catered to each patient’s particular requirements by examining patient data, including dental records, medical histories, and other pertinent factors. This can assist dentists in selecting the best course of therapy and enhance the results of dental procedures.
Dentistry technologies:
The creation of novel dental materials and technologies is another area where AI is being used in dentistry. AI can assist researchers in creating stronger, more resilient, and more biocompatible materials that are better suitable for dental restorations by simulating the behavior of materials in the mouth.
Whitening teeth with AI in dentistry:
Teeth bleaching can benefit from AI technology, which can help dentists diagnose and plan treatments for discolored teeth. Digital images of the teeth can be analyzed by AI programs to determine the type and degree of discoloration, enabling dentists to create more individualized and successful treatment plans.
AI, for instance, can examine images of teeth and determine their precise hue and shade as well as any regions of discoloration or staining. Based on this data, AI can assist dentists in selecting the best teeth-whitening method, such as at-home treatments, in-office procedures, or a mix of both.
AI can also help with tracking the development of teeth bleaching. AI can monitor the progress of the teeth-whitening procedure and adjust as necessary to guarantee the best results by examining digital images of the teeth over time.
Will AI replace dentists?
Will AI take over dentist? Some dentists may be concerned about being replaced by robots, but we anticipate those concerns to fade as the AI assistant’s convenience and productivity become widely recognized. Because AI technologies do not provide care, it will not replace dentists; rather, it will help them. We foresee widespread adoption of dental AI in the coming years; in fact, it will become an expected complement to the x-ray camera. We anticipate that treatment prices will become less unpredictable and variable, and that patients will have greater trust in the objectivity of their dentists.
Longer term, we expect to see more use of population-wide “big data,” including dental data, to provide new insights into general health and its links to dental health. When privacy concerns are addressed, AI should work in tandem with health record digitization to enhance patient care both within and outside of the field of dentistry.
Final words about AI in dentistry:
Overall, applying AI to dentistry has the potential to enhance treatment planning, increase diagnosis precision and speed, and enhance the results of dental procedures. AI is probably going to become more and more significant in the future of dental treatment as technology develops.
Dentistry is well-positioned to benefit from AI’s capabilities. Everyone who visits a dentist has X-rays taken at some point, so there are likely far more oral X-rays than any other type. These annotated radiographic images are being used to educate AI systems what healthy and unhealthy teeth look like and how to tell the difference.
Indeed, the day will come — perhaps sooner than we think — when AI systems in dental offices will not only spot immediate dental concerns, but will also anticipate the effect those concerns may have on a patient’s overall health through analysis of medical records. Other areas of healthcare were the first to move toward a digital future, but it now appears that dentistry is heading the way.
How much do dental implants cost in Iran?
In Iran, we use the highest quality dental implants and the components used in these implants are made in countries such as the United States, Germany, Switzerland and Korea. By these notes and in general for each dental implant in Iran, about 600$-700$, you have to pay.

